Project information
- Keywords: Retinal, Graph, Machine Learning, Photoisomerization, NAMD, AIMD
- Project date: 30 November, 2023
- Publication URL: Link to article
- Journal: The Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling
Project Details
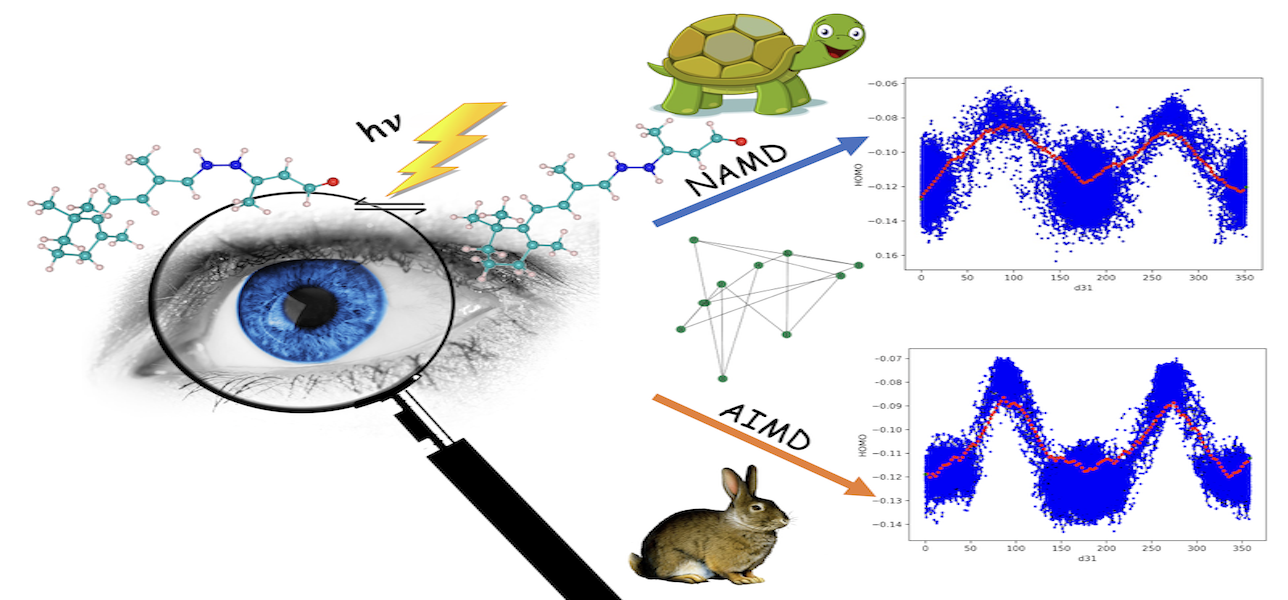
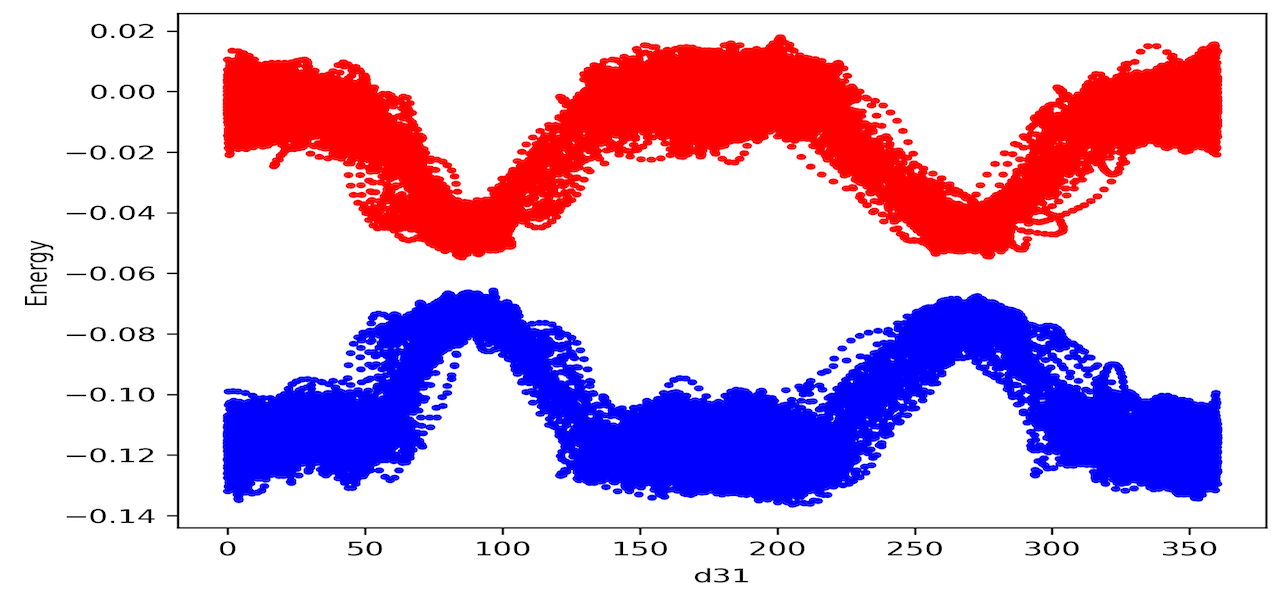
Unraveling the complexities of photoinduced reactions poses a formidable challenge. Recently, a combination of graph theory-based machine learning and non-adiabatic molecular dynamics (NAMD) has been employed to derive the global reaction coordinate for azobenzene photoisomerization. However, NAMD simulations are computationally expensive due to the need for calculating non-adiabatic coupling vectors at each time step. In this study, we demonstrate that ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) can serve as a cost-effective alternative to NAMD by selecting an appropriate initial condition for the simulation. Applying this methodology to ascertain a plausible global reaction coordinate for retinal photoisomerization crucial to human vision, our approach, based on mutual information (MI) between internal coordinates and HOMO energy, shows a similar trend in rank-ordering internal coordinates compared to NAMD. Our findings indicate that AIMD-based machine learning is a computationally more affordable approach than NAMD for studying reaction coordinates.