Project information
- Keywords: Azobenzene, G-quadruplex, QM/MM, Force Field, PES
- Project date: 09 November, 2020
- Publication URL: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP04392C
- Journal: Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
Project Details
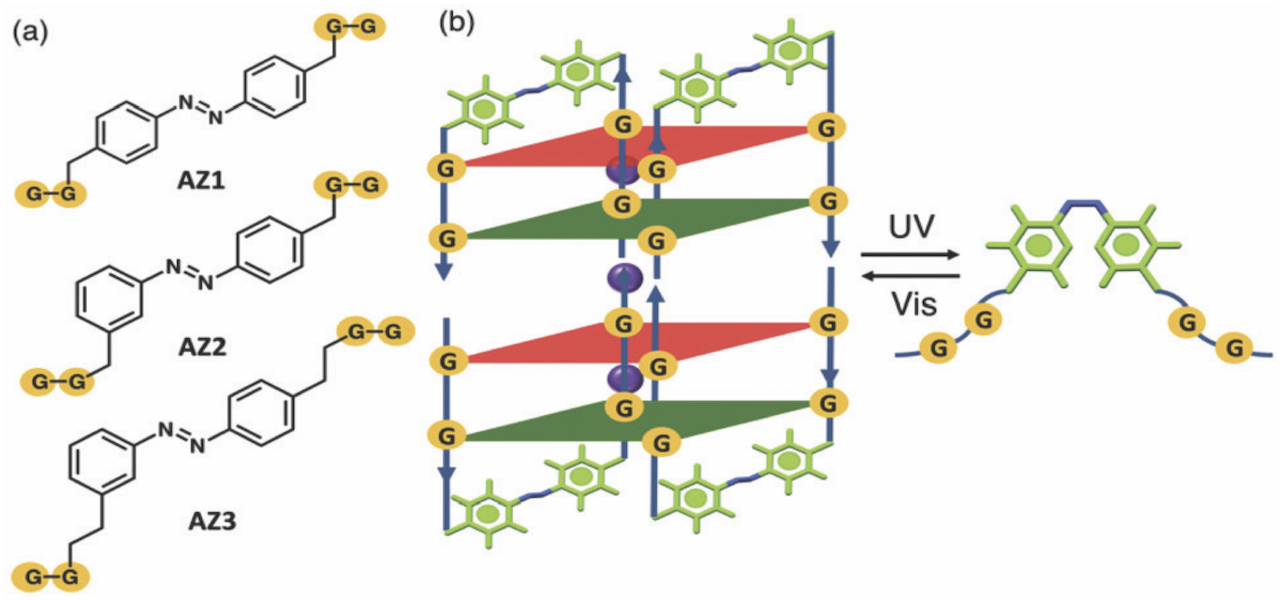
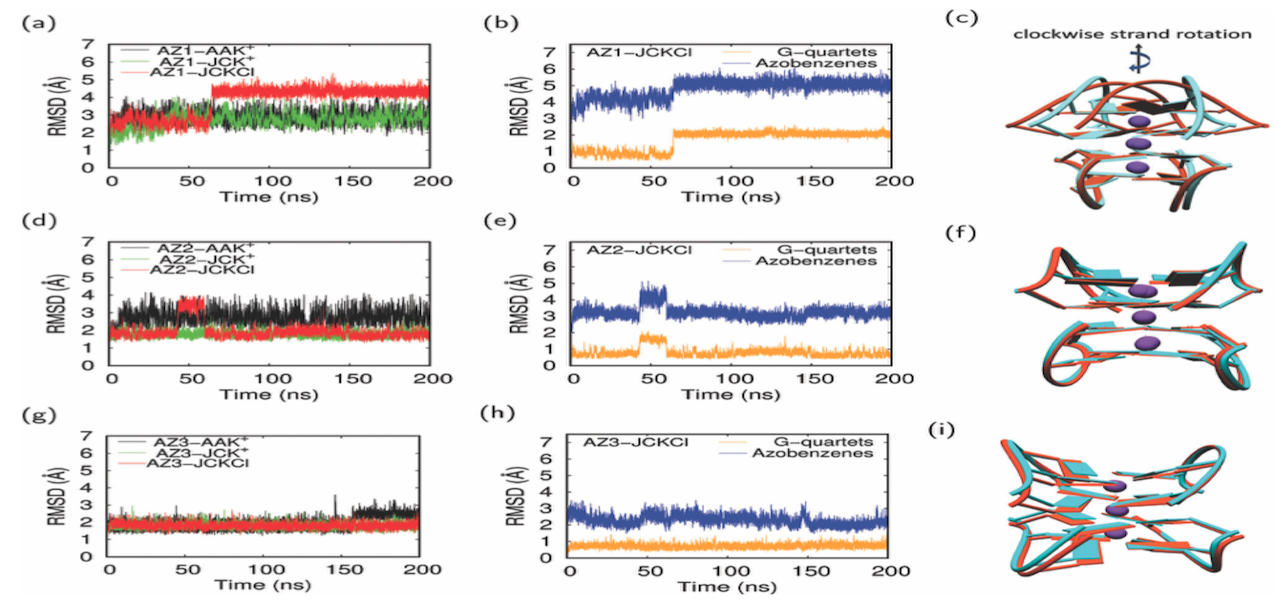
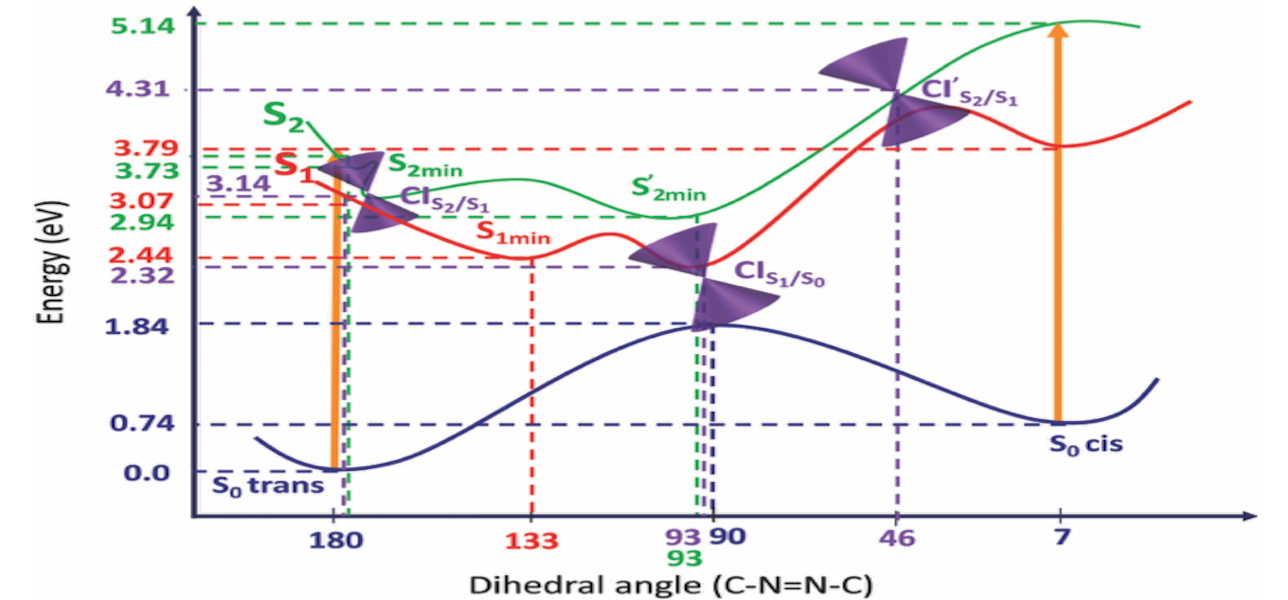
Examining the integration of photoswitches into DNA G-quadruplexes for nanodevice development, this study, utilizing a quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) approach, explored the impact of size and substitution patterns of azobenzene derivatives (AZ1, AZ2, AZ3) on the excitation energies of the smallest photoswitchable G-quadruplex. Findings revealed minimal influence on the photoisomerization mechanism, aligning with experimental results. Molecular dynamics simulations highlighted structural stability differences, with AZ1 displaying greater flexibility. QM/MM absorption spectra simulations emphasized thermal fluctuations' significant role over the G-quadruplex environment. The position of azobenzene linkers in edgewise loops above G-quartets was identified as a key factor. These theoretical insights support recent studies on photoswitchable G-quadruplex motifs.