Project information
- Keywords: QM/MM, Drug Design, Free Energy, SARS-CoV-2, Main Protease
- Project date: 09 June, 2023
- Publication URL: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c02229
- Journal: The Journal of the American Chemical Society
Project Details
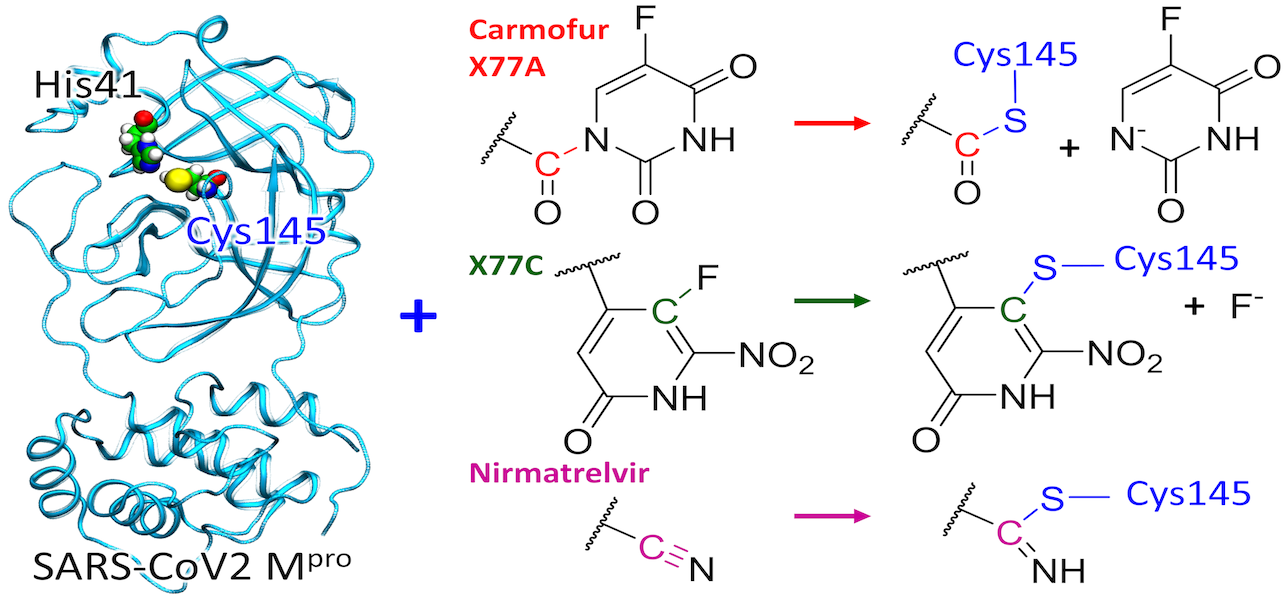
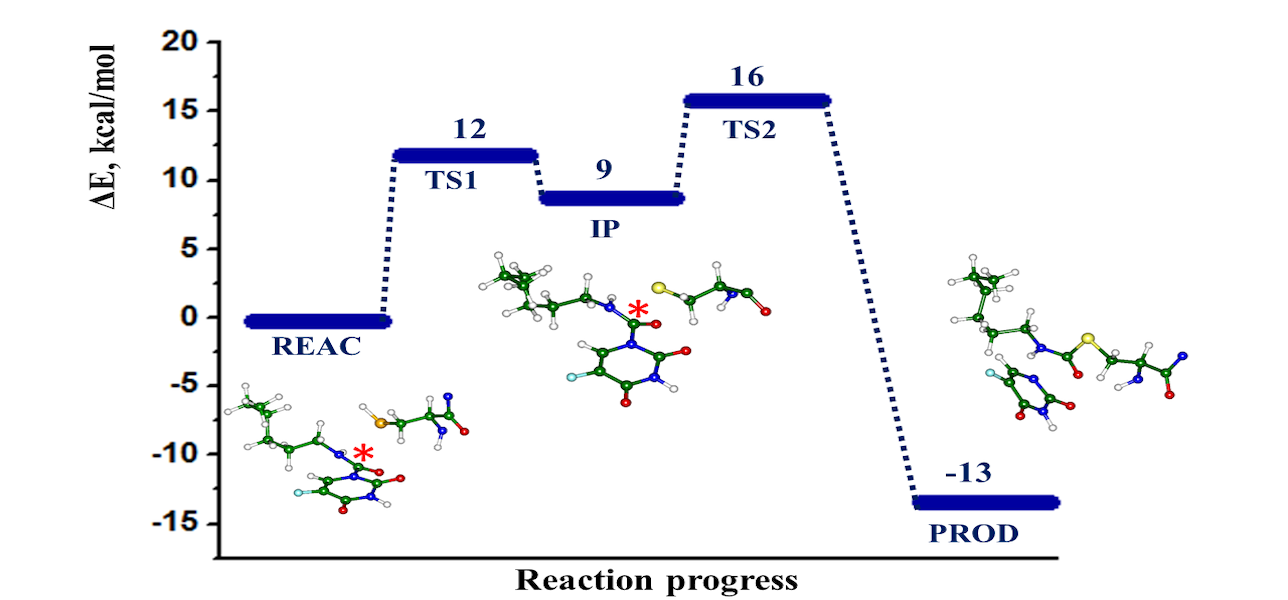
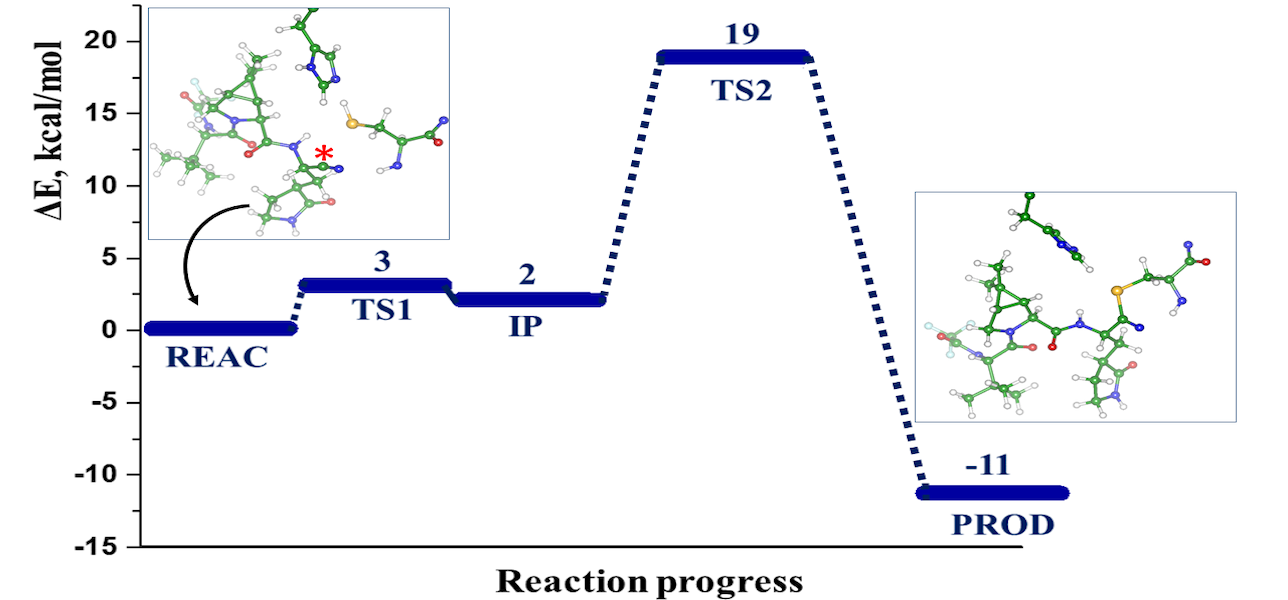
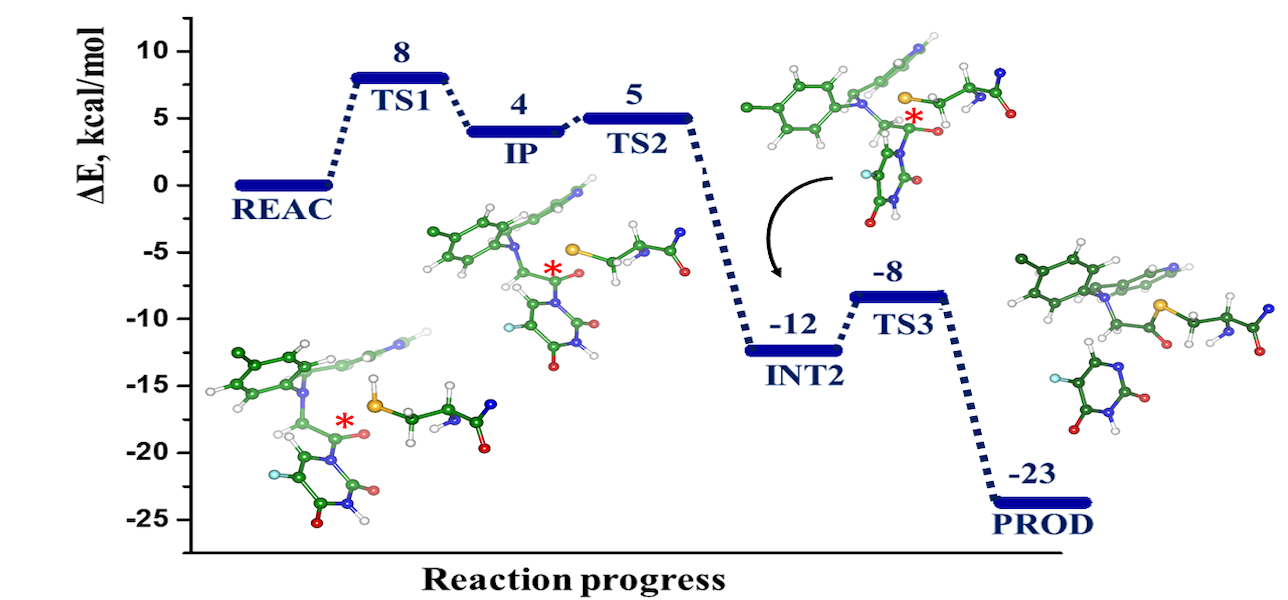
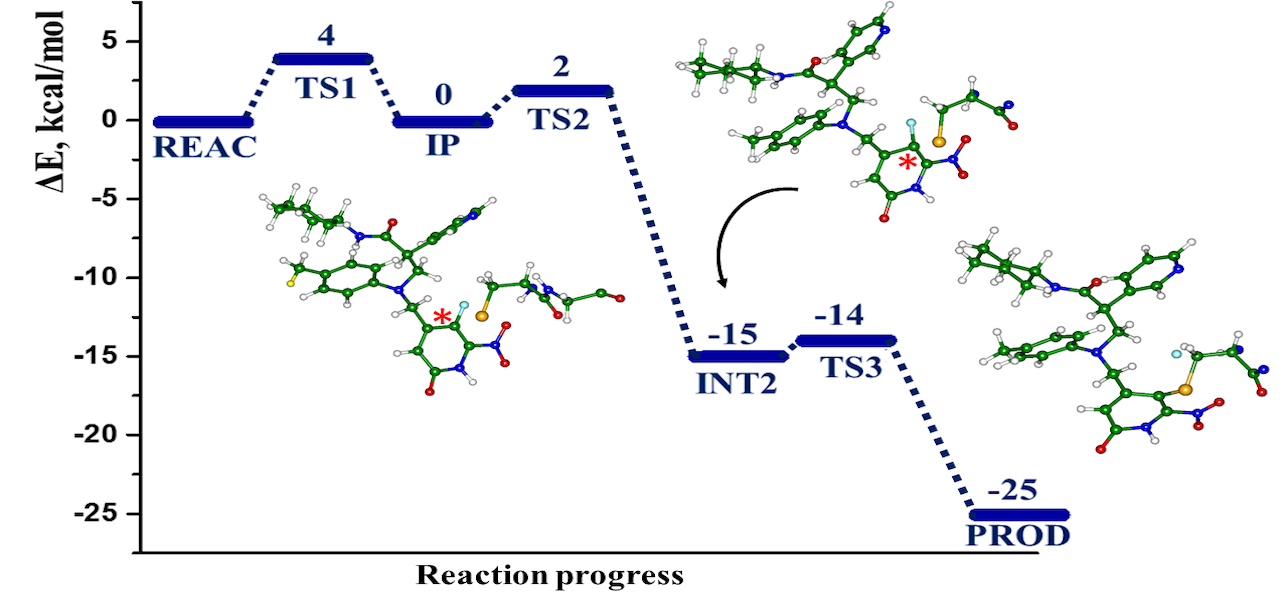
The computational modeling results of the interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (MPro) and four potential covalent inhibitors are presented. Carmofur and nirmatrelvir, known experimental inhibitors, along with computationally designed X77A and X77C, were investigated. Quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) simulations revealed that all compounds form covalent adducts with the catalytic cysteine Cys 145 of MPro. The mechanistic analysis indicated three distinct mechanisms, initiated by a nucleophilic attack of the thiolate group from the catalytic dyad Cys145-His41. Carmofur and X77A showed covalent binding with the formation of a fluoro-uracil leaving group, while X77C followed the SNAr mechanism. Nirmatrelvir, featuring a reactive nitrile group, led to the formation of a covalent thioimidate adduct. These insights contribute to the search for effective inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 enzymes.